Introduction to the scimetr package
UDC Ranking’s Group
scimetr 1.2.0: 2026-03-02
Source:vignettes/scimetr.Rmd
scimetr.Rmd## scimetr: Analysis of Scientific Publication Data with R,
## version 1.2.0 (built on 2026-03-01).
## Copyright (C) UDC Rankings Group 2017-2026.
## Type `help(scimetr)` for an overview of the package or
## visit https://rubenfcasal.github.io/scimetr.This vignette illustrates the use of the scimetr
package for performing bibliometric analyses using datasets exported
from Web of Science, highlighting the main workflows and
functionalities. The package provides tools for scientometric and
bibliometric research, including routines to import bibliographic
records from Clarivate
Analytics Web of Science (WoS) and conduct bibliometric
analyses.
A list of other useful R packages for this type of analysis is available here.
Installation
Since the package is not yet available on CRAN, you need to install the development version from the GitHub repository rubenfcasal/scimetr:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("rubenfcasal/scimetr")Alternatively, Windows users may install the corresponding scimetr_X.Y.Z.zip file in the releases section of the github repository. It is recommended to first install its dependencies:
# Dependencies
install.packages(c("dplyr", "tidyr", "stringr", "ggplot2", "scales", "rlang"))
# Last released version
install.packages("https://github.com/rubenfcasal/scimetr/releases/download/v1.1.0/scimetr_1.1.0.zip", repos = NULL)Once the package is installed, it can be loaded as usual.
Bibliographic data
We will focus exclusively on importing publication data from WoS in text format. First, you need to download the corresponding files from the WoS website, for example, by following the steps described here.
Loading WoS data from a directory
WoS files (which by default are limited to 500 records each) can be automatically loaded from a subdirectory:
dir("UDC_2018-2023 (01-02-2024)", pattern = "*.txt")## [1] "savedrecs01.txt" "savedrecs02.txt" "savedrecs03.txt" "savedrecs04.txt"
## [5] "savedrecs05.txt" "savedrecs06.txt" "savedrecs07.txt" "savedrecs08.txt"
## [9] "savedrecs09.txt" "savedrecs10.txt"To combine the files into a data.frame, the
import_wos() function is used:
wos.data <- import_wos("UDC_2018-2023 (01-02-2024)")Next, the database must be created using the db_bib()
function, as shown later.
Example data
The package includes the example dataset wosdf (obtained
using the import_wos() function), corresponding to a WoS
search by the Affiliation field of Universidade da Coruña (UDC)
(Affiliation: OG = Universidade da Coruna) in the research area
"Mathematics" during the years 2018–2023.
All data tables have an associated variable.labels
attribute with the variable labels. These will be displayed below the
variable names when viewed in RStudio
(e.g. View(wosdf)).
wos.labels <- attr(wosdf, "variable.labels")
knitr::kable(head(data.frame(wos.labels)),
col.names = c("Variable", "Label")
)| Variable | Label |
|---|---|
| PT | Publication Type |
| AU | Author |
| AF | Author Full Name |
| TI | Article Title |
| SO | Source Title |
| SE | Book Series Title |
…
A full list of the variables used in the database tables is shown in the final section Variable list of this document.
Bibliographic database
scimetr uses lists with data.frame
components as relational databases.
To create the bibliographic
database, use the db_bib() function (the result is a
wos.db-class S3 object):
## [1] "Docs" "Authors" "AutDoc" "OI" "OIDoc"
## [6] "RI" "RIDoc" "Categories" "CatSour" "Areas"
## [11] "AreaSour" "Addresses" "AddAutDoc" "Affiliations" "AffDoc"
## [16] "Sources" "WSIndex" "SourWSI" "label" "date"Summaries
You can generate either global summaries or yearly summaries of your database.
Global summary
The summary() method of a bibliographic database
(summary.wos.db()), provides an overview of the entire
database, including total documents, authors, journals, citations, and
other aggregated statistics.
## Number of documents: 293
## Authors: 504
## Period: 2018 - 2023
##
## Document types:
## Documents
## Article 254
## Article; Early Access 1
## Article; Proceedings Paper 2
## Correction 7
## Editorial Material 21
## Review 8
##
## Number of authors per document:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 1.00 3.00 3.00 3.63 4.00 13.00
##
## Number of documents per author:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 1.00 1.00 1.00 2.11 2.00 23.00
##
## Number of times cited:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.00 1.00 3.00 5.87 7.00 123.00
##
## Indexes:
## H G
## 19 27
##
## Status:
## Highly Cited Hot Papers
## 1 0
##
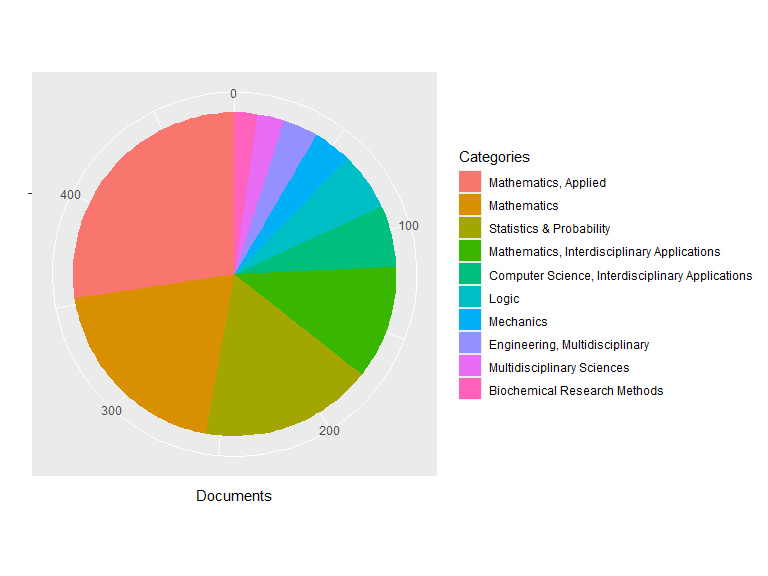
## Top Categories:
## Documents
## Mathematics, Applied 133
## Mathematics 96
## Statistics & Probability 84
## Mathematics, Interdisciplinary Applications 55
## Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications 30
## Logic 28
## Mechanics 19
## Engineering, Multidisciplinary 17
## Multidisciplinary Sciences 13
## Biochemical Research Methods 11
## Others 104
##
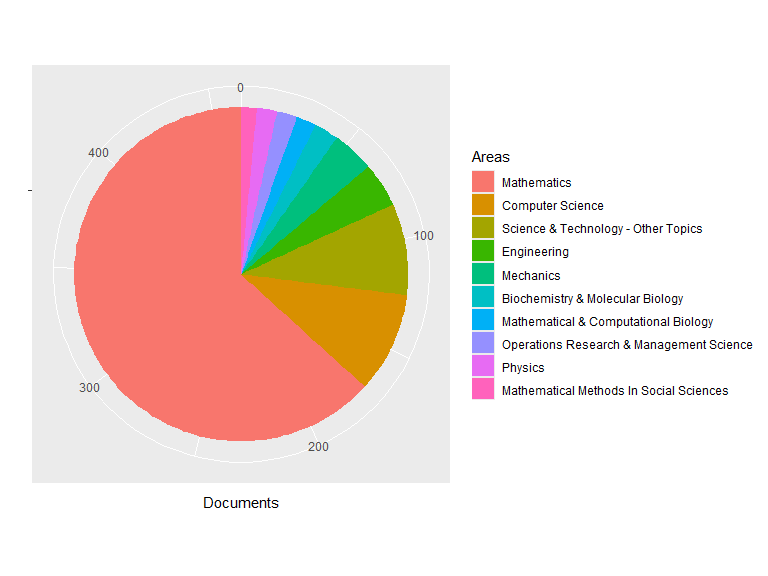
## Top Areas:
## Documents
## Mathematics 293
## Computer Science 45
## Science & Technology - Other Topics 41
## Engineering 20
## Mechanics 19
## Biochemistry & Molecular Biology 11
## Mathematical & Computational Biology 9
## Operations Research & Management Science 9
## Physics 9
## Mathematical Methods In Social Sciences 7
## Others 37
##
## Top Journals:
## Documents
## Log. J. IGPL 28
## Mathematics 21
## Test 17
## Appl. Math. Comput. 9
## Complexity 9
## IEEE-ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 7
## J. Math. Anal. Appl. 7
## Comput. Math. Appl. 6
## J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6
## Arch. Comput. Method Eng. 5
## Others 178
##
## Top Countries:
## Documents
## Spain 293
## France 20
## UK 18
## USA 17
## Italy 13
## Chile 9
## Ecuador 9
## Portugal 8
## Argentina 6
## Uruguay 6
## Others 46
##
## International colaboration documents (Spain): 134Yearly summary
The summary_year() method breaks down the summary by
year, showing trends over time in publications, citations, and
other key metrics.
res2 <- summary_year(db)
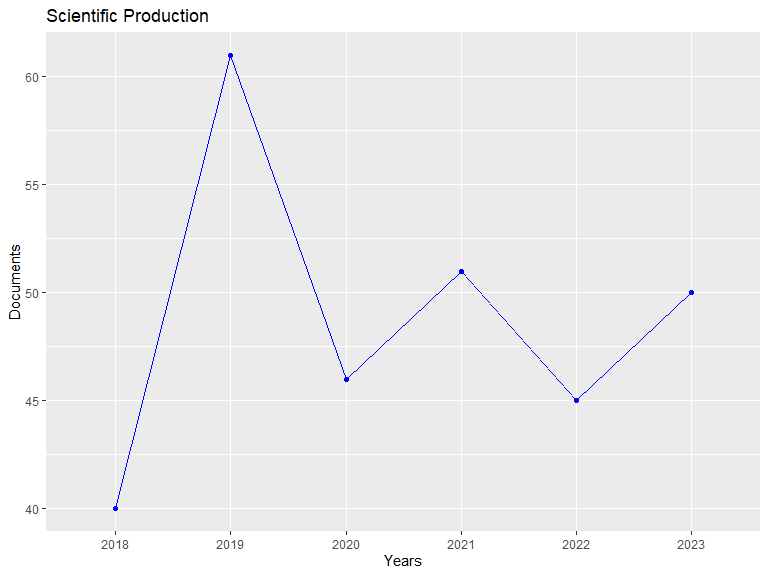
res2## Annual Scientific Production:
## Documents
## 2018 40
## 2019 61
## 2020 46
## 2021 51
## 2022 45
## 2023 50
##
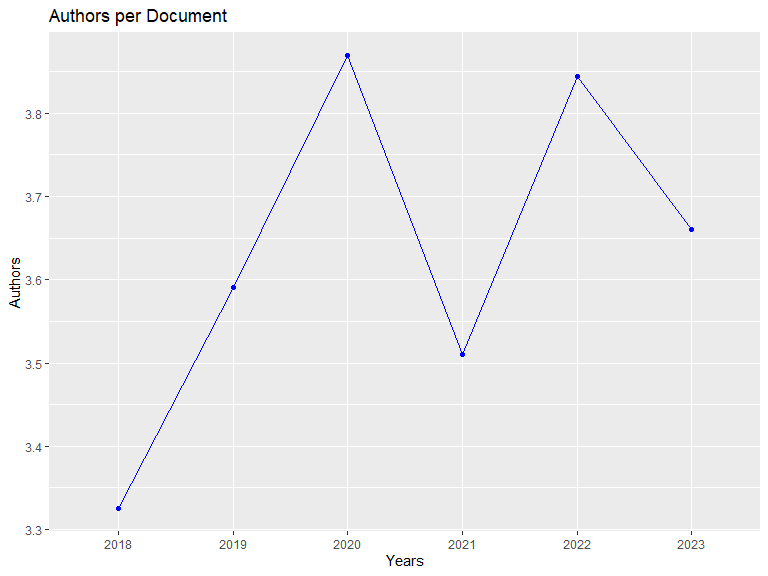
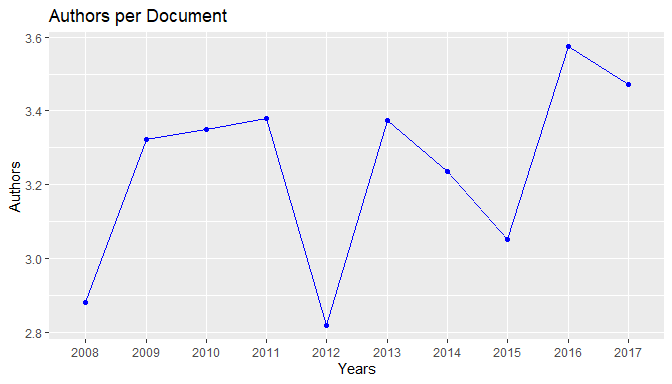
## Annual Authors per Document:
## PY Mean Median
## 2018 3.3250 3.5
## 2019 3.5902 3.0
## 2020 3.8696 3.0
## 2021 3.5098 3.0
## 2022 3.8444 3.0
## 2023 3.6600 3.0
##
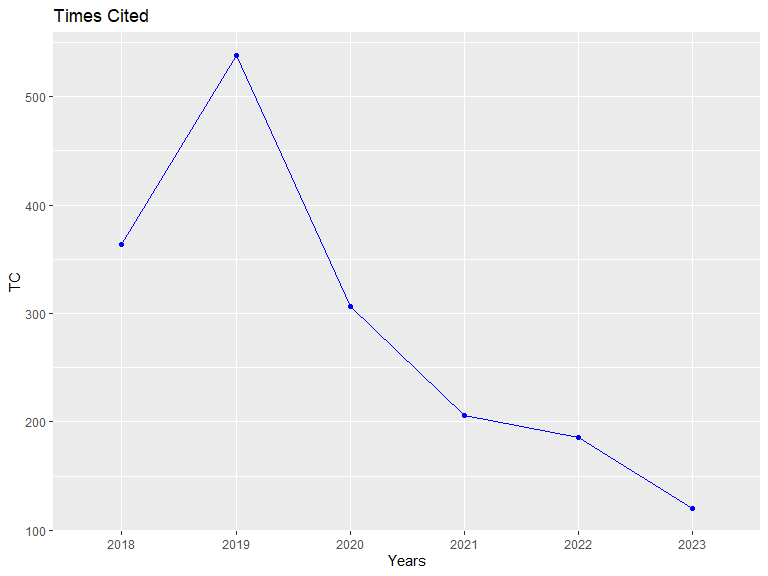
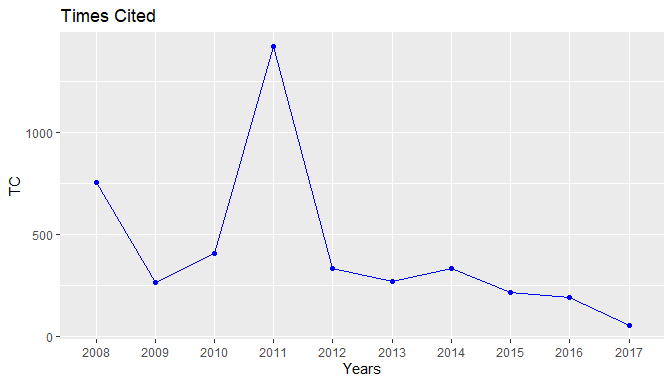
## Annual Times Cited:
## PY Cites Mean Median
## 2018 364 9.1000 5.0
## 2019 538 8.8197 5.0
## 2020 306 6.6522 3.0
## 2021 206 4.0392 3.0
## 2022 186 4.1333 2.0
## 2023 120 2.4000 1.5
##
## Status:
## PY Highly Cited Hot Paper
## 2018 0 0
## 2019 1 0
## 2020 0 0
## 2021 0 0
## 2022 0 0
## 2023 0 0Visualizations
The ggplot2
package is used to create a wide variety of visualizations from the
database.
There are three main types of plots you can create:
Database plots (
plot(db)).Summary plots (
plot(summary(db)).Yearly summary plots (
plot(summary_year(db))).
Note: All plot() methods invisible return a list with
the generated ggplot2 objects (use
plot = FALSE to avoid plotting).
Database plots
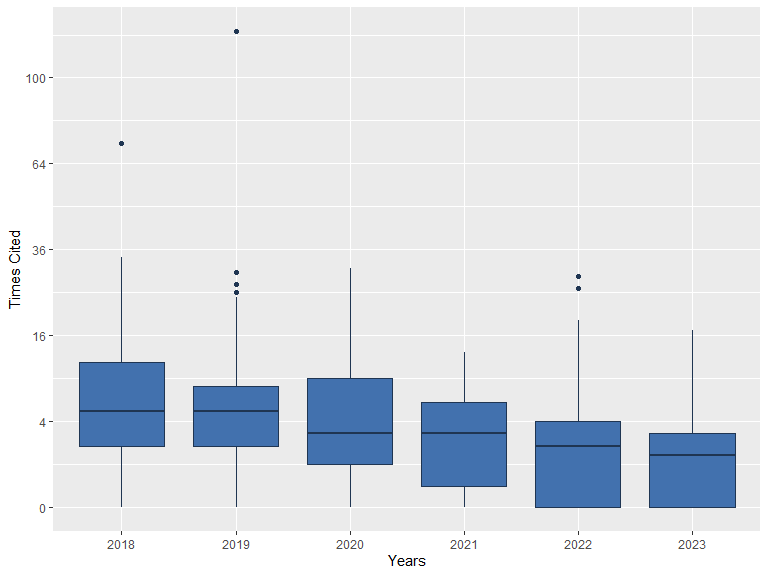
The plot() method of a bibliographic database
(plot.wos.db()) provides a general visualization of its
contents.
plot(db)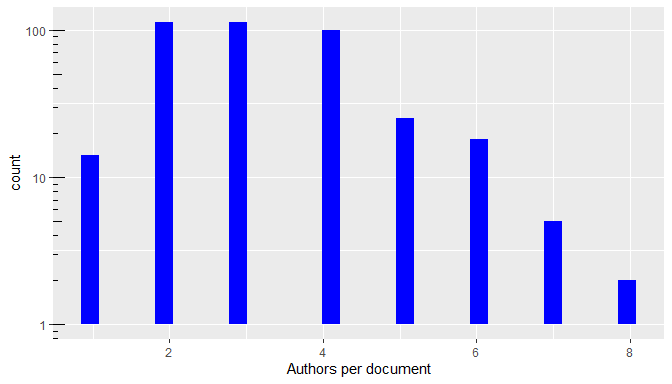
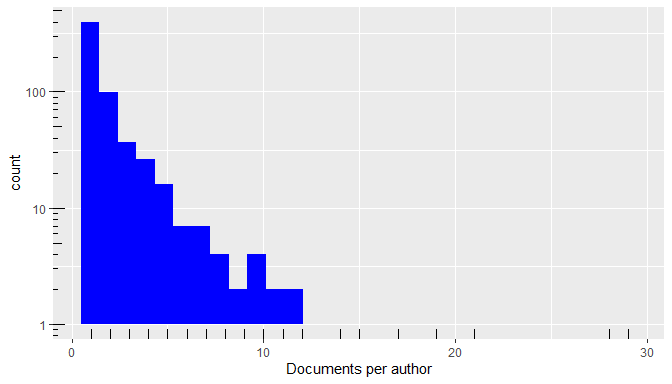
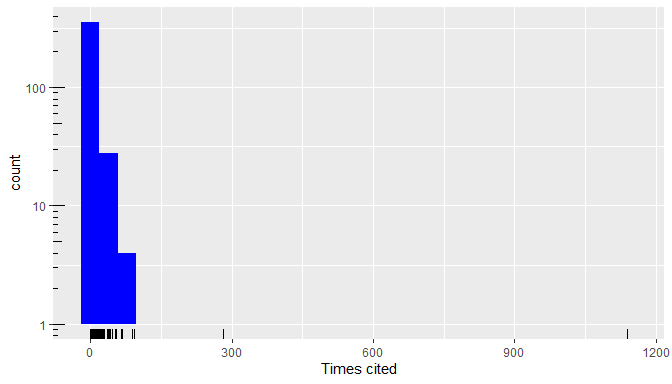
Summary plots
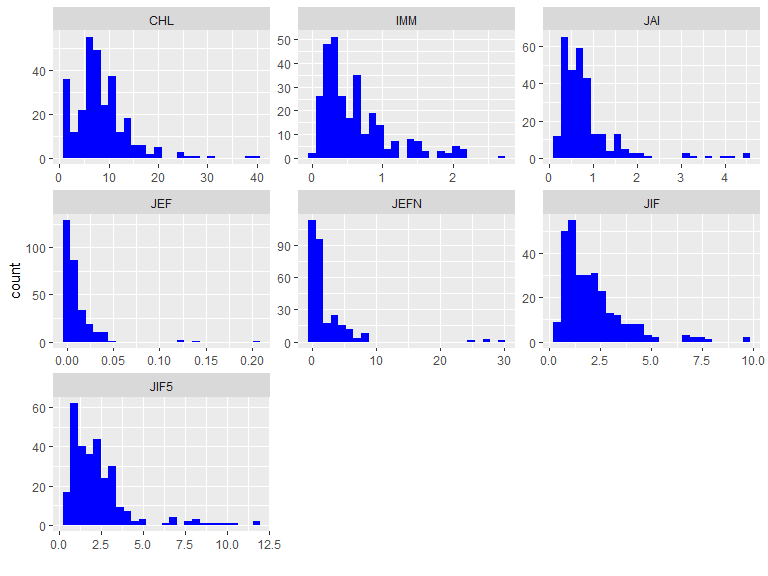
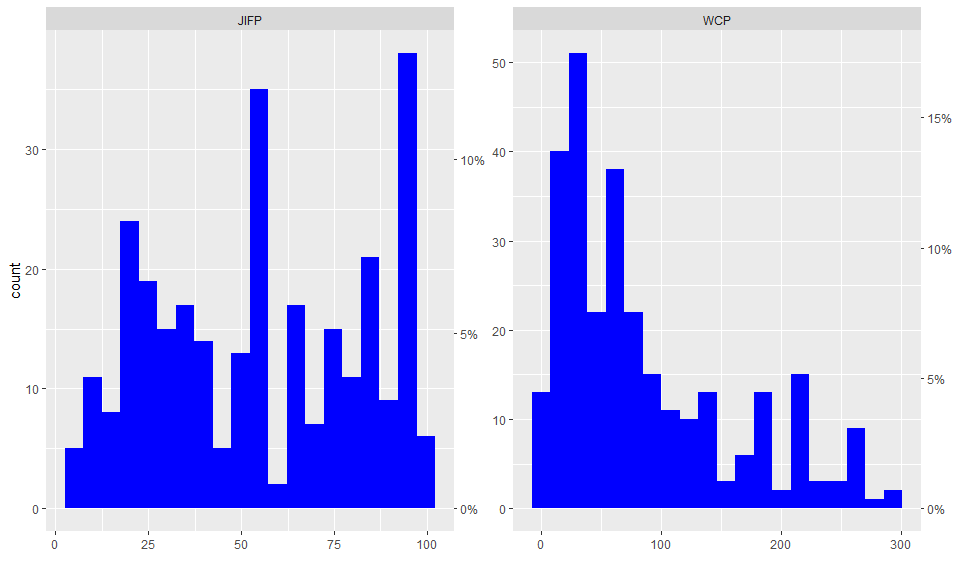
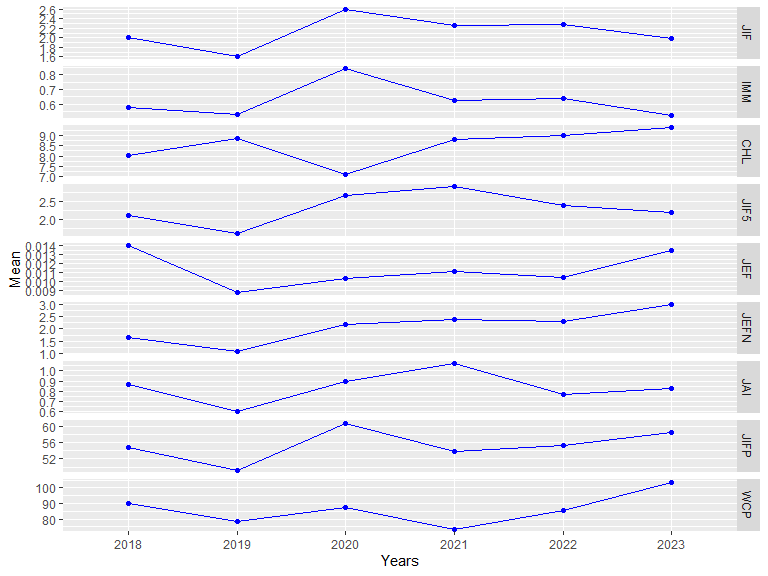
The plot method of a summary result
(plot.summary.wos.db()) visualizes the results generating
different types of plots: standard bar, line plots or Pie charts
(pie = TRUE).
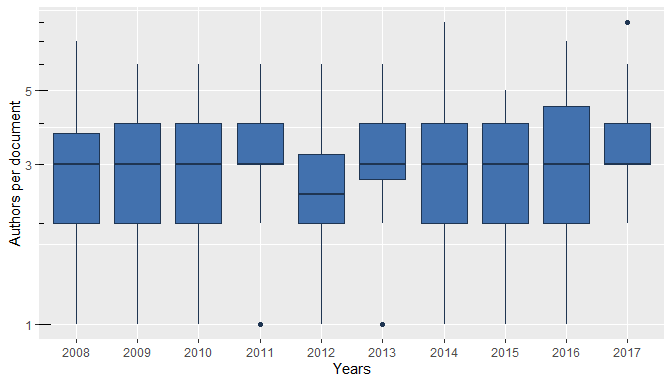
plot(res1)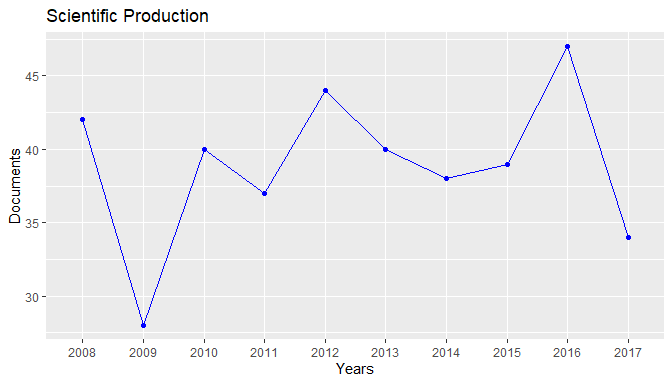
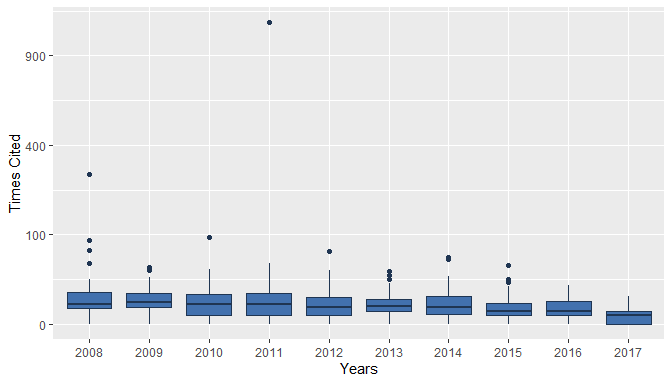
plot(res1, pie = TRUE)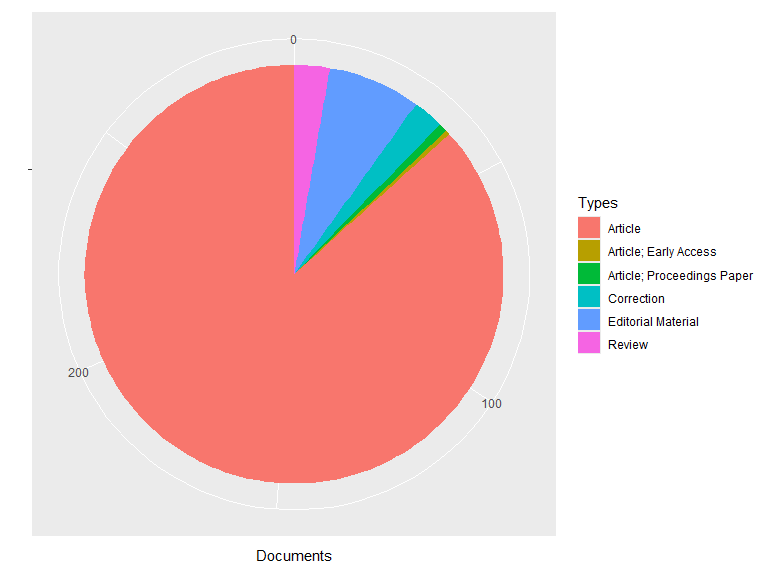
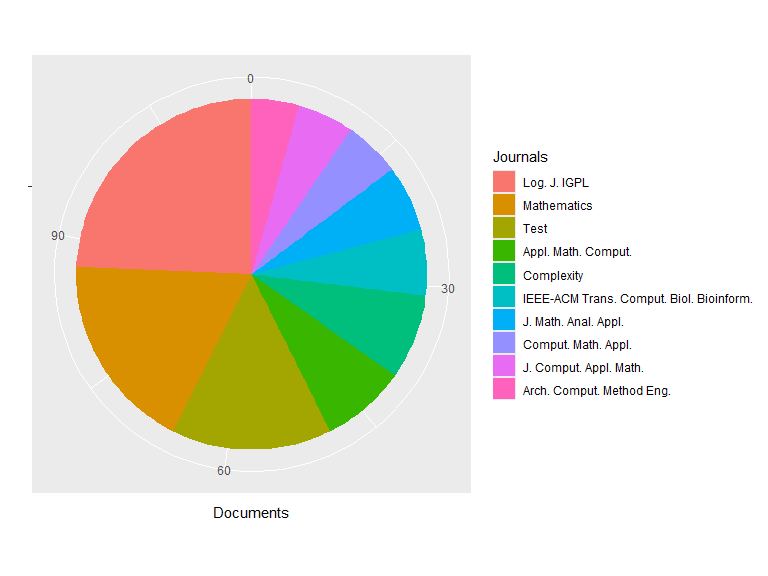
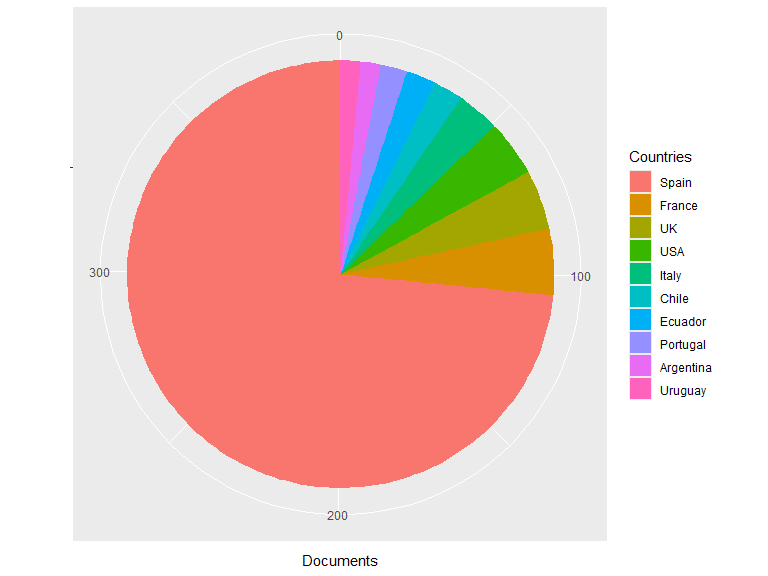
Filtering
To filter elements (entities) of the database, you can use the
functions get_id_<table>() to retrieve identification
codes (IDs or entity key values). Any variable from the corresponding
<table> may be used (multiple conditions are combined
with &; see e.g. dplyr::filter()).
Typically, these functions are combined together with the
get_id_docs() function to obtain document IDs, which are
finally used in argument filter of summary functions to
filter documents in results.
Retrieving element IDs (entity key values)
-
get_id_authors(): Retrieve author IDs (codes)Search for a specific author:
ida <- get_id_authors(db, AF == "Cao, Ricardo") ida## Cao, Ricardo Cao, Ricardo ## 11 260Search by partial name match:
idas <- get_id_authors(db, grepl("Cao", AF)) idas## Cao, Ricardo Cao-Rial, M. T. Cao, Ricardo Cao, R. ## 11 80 260 328 ## Cao Abad, Ricardo Cao-Rial, M. T. ## 501 504 -
get_id_areas(): Retrieve codes for research areasget_id_areas(db, SC == "Mathematics")## Mathematics ## 16get_id_areas(db, SC == "Mathematics" | SC == "Computer Science")## Computer Science Mathematics ## 6 16 -
get_id_categories(): Retrieve category codesget_id_categories(db, grepl("Mathematics", WC))## Mathematics ## 148 ## Mathematics, Applied ## 149 ## Mathematics, Interdisciplinary Applications ## 150 -
get_id_sources(): Retrieve source codes (journals, books, or collections)idtest <- get_id_sources(db, SO == "TEST") idtest## TEST ## 6knitr::kable(t(db$Sources[idtest, ]), caption = "Test journal", col.names = c("Variable", "Value") )Test journal Variable Value ids 6 PT Journal SO TEST SE NA BS NA LA English PU SPRINGER PI NEW YORK PA ONE NEW YORK PLAZA, SUITE 4600, NEW YORK, NY, UNITED STATES SN 1133-0686 EI 1863-8260 BN NA J9 TEST-SPAIN JI Test # get_id_sources(db, JI == 'Test')
Retrieving documents IDs (by authors, journals, etc.)
The IDs retrieved above can be combined in
get_id_docs():
idocs <- get_id_docs(db, id_authors = ida)
idocs## [1] 6 14 66 94 102 104 148 162 164 170 171 187 225 286 287 288The document IDs can be used as filters, for example, in
summary.wos.db().
Filtered Summaries
Get a summary for one or more authors:
summary(db, idocs)## Number of documents: 16
## Authors: 21
## Period: 2019 - 2023
##
## Document types:
## Documents
## Article 10
## Editorial Material 5
## Review 1
##
## Number of authors per document:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 1.00 2.00 3.00 2.81 3.25 5.00
##
## Number of documents per author:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 1.00 1.00 1.00 2.14 2.00 9.00
##
## Number of times cited:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.00 0.00 2.50 11.81 6.75 123.00
##
## Indexes:
## H G
## 5 13
##
## Status:
## Highly Cited Hot Papers
## 1 0
##
## Top Categories:
## Documents
## Statistics & Probability 15
## Operations Research & Management Science 2
## Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications 1
## Mathematical & Computational Biology 1
## Mathematics 1
## Medical Informatics 1
## Medicine, Research & Experimental 1
## Public, Environmental & Occupational Health 1
##
## Top Areas:
## Documents
## Mathematics 16
## Operations Research & Management Science 2
## Computer Science 1
## Mathematical & Computational Biology 1
## Medical Informatics 1
## Public, Environmental & Occupational Health 1
## Research & Experimental Medicine 1
##
## Top Journals:
## Documents
## Test 4
## J. Nonparametr. Stat. 2
## J. Multivar. Anal. 2
## SORT-Stat. Oper. Res. Trans. 2
## Mathematics 1
## Comput. Stat. 1
## Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 1
## Stat. Med. 1
## J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 1
## Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Comput. Stat. 1
##
## Top Countries:
## Documents
## Spain 16
## France 3
## Uruguay 2
## Belgium 1
## Canada 1
## Mexico 1
## Switzerland 1
## USA 1
##
## International colaboration documents (Spain): 7Get a year-by-year summary for one or more authors:
summary_year(db, idocs)## Annual Scientific Production:
## Documents
## 2019 6
## 2020 2
## 2021 3
## 2022 3
## 2023 2
##
## Annual Authors per Document:
## PY Mean Median
## 2019 3.1667 3.5
## 2020 3.0000 3.0
## 2021 2.6667 3.0
## 2022 2.6667 3.0
## 2023 2.0000 2.0
##
## Annual Times Cited:
## PY Cites Mean Median
## 2019 166 27.667 10.5
## 2020 11 5.500 5.5
## 2021 6 2.000 0.0
## 2022 6 2.000 2.0
## 2023 0 0.000 0.0
##
## Status:
## PY Highly Cited Hot Paper
## 2019 1 0
## 2020 0 0
## 2021 0 0
## 2022 0 0
## 2023 0 0Author metrics
Retrieve metrics for multiple authors:
author_metrics(db, idas)## H G
## Cao, Ricardo 3 9
## Cao-Rial, M. T. 4 5
## Cao, Ricardo 4 5
## Cao, R. 0 0
## Cao Abad, Ricardo 1 2
## Cao-Rial, M. T. 0 0Bibliographic database with JCR metrics
We can extends the bibliographic database by adding JCR metrics to sources, per year and WoS category.
Import JCR data from WoS
Excel files with JCR data (avaliable from WoS) can be automatically loaded from a subdirectory:
dir("JCR_download", pattern = "*.xlsx")## [1] "JCR_SCIE_2018.xlsx" "JCR_SCIE_2019.xlsx" "JCR_SCIE_2020.xlsx"
## [4] "JCR_SCIE_2021.xlsx" "JCR_SCIE_2022.xlsx" "JCR_SCIE_2023.xlsx"
## [7] "JCR_SSCI_2018.xlsx" "JCR_SSCI_2019.xlsx" "JCR_SSCI_2020.xlsx"
## [10] "JCR_SSCI_2021.xlsx" "JCR_SSCI_2022.xlsx" "JCR_SSCI_2023.xlsx"To combine the files into a relational database, the
db_jcr() function is used:
jcr <- db_jcr("JCR_download")Add JCR data to a bibliographic database
The JCR data can be combined with a bibliographic database by using
the add_jcr() function:
dbjcr <- add_jcr(db, jcr)Two additional tables, JCRSour and
JCRCatSour, are added to the bibliographic database (the
result is a wos.jcr-class S3 object).
The database resulting from this particular example is provided as a
dataset of the scimetr package:
names(dbjcr)## [1] "Docs" "Authors" "AutDoc" "OI" "OIDoc"
## [6] "RI" "RIDoc" "Categories" "CatSour" "Areas"
## [11] "AreaSour" "Addresses" "AddAutDoc" "Affiliations" "AffDoc"
## [16] "Sources" "WSIndex" "SourWSI" "label" "export.date"
## [21] "JCRSour" "JCRCatSour"
class(dbjcr)## [1] "wos.jcr" "wos.db"Summaries
Auxiliary functions are available to perform database queries:
-
get_jcr(): combines document indexes with their source JCR metrics per year.## idd ids PY JIF IMM CHL JIF5 JEF JEFN JAI ## 1 1 1 2021 1.673 0.165 4.9 11.808 0.01332 2.86423 4.500 ## 2 2 2 2018 2.896 1.169 4.7 2.344 0.00585 0.69599 0.707 ## 3 3 3 2023 2.300 0.900 1.9 2.200 0.03686 8.10075 0.374 ## 4 4 4 2023 4.400 1.000 3.2 3.600 0.00847 1.86316 0.691 ## 5 5 5 2023 4.400 1.000 10.0 7.600 0.12386 27.21696 3.056 ## 6 6 6 2023 1.200 0.200 7.7 2.200 0.00235 0.51687 1.225 -
get_jcr_cat()combines document indexes with their source JCR metrics per year and WoS category (ifbest = TRUE, only the results for the WoS category with the best ranking for each document are returned).head(get_jcr_cat(dbjcr, best = TRUE))## idd ids PY idc WCR JIFQ JIFP WE WCP WCT ## 1 1 1 2021 46 0.13514 Q4 13.840 SCIE 97 112 ## 2 2 2 2018 46 0.65714 Q2 65.566 SCIE 37 106 ## 3 3 3 2023 148 0.95910 Q1 95.800 SCIE 21 490 ## 4 4 4 2023 46 0.78107 Q1 77.900 SCIE 38 170 ## 5 5 5 2023 26 0.78613 Q1 78.400 SCIE 38 174 ## 6 6 6 2023 237 0.56287 Q2 56.300 SCIE 74 168
The summary methods combine the above queries and generate global
summaries or yearly summaries of a bibliographic database with JCR
metrics (if all = TRUE, the corresponding
wos.db-class results are also generated).
res1 <- summary(dbjcr)
res1## JCR metrics:
## JIF IMM CHL JIF5 JEF JEFN JAI JIFP WCP
## Min. 0.4 0.00 1.1 0.48 0.00042 0.053 0.18 2.8 5
## 1st Qu. 1.0 0.26 5.6 1.00 0.00226 0.381 0.42 28.6 31
## Median 1.7 0.45 7.7 1.87 0.00500 0.848 0.66 56.3 58
## Mean 2.1 0.62 8.6 2.30 0.01119 2.060 0.83 55.1 86
## 3rd Qu. 2.6 0.83 10.4 2.73 0.01412 2.352 0.89 82.6 126
## Max. 9.7 2.69 39.5 11.81 0.20530 29.627 4.50 97.6 298
## NA's 1.0 1.00 1.0 2.00 1.00000 1.000 2.00 1.0 1
##
## Documents in JCR: 292 (99.66%)
## Documents in Q1: 90 (30.82% of JCR)
## Documents in D1: 50 (17.12% of JCR)
## Documents in top 3 journals: 0 (0% of JCR)
res2 <- summary_year(dbjcr)
res2## Mean of JCR metrics:
## PY JIF IMM CHL JIF5 JEF JEFN JAI JIFP WCP
## 2018 2.01 0.579 8.03 2.11 0.01397 1.66 0.864 54.8 89.7
## 2019 1.60 0.527 8.85 1.61 0.00876 1.07 0.605 49.3 78.4
## 2020 2.59 0.841 7.09 2.68 0.01030 2.16 0.899 60.8 87.2
## 2021 2.27 0.624 8.81 2.92 0.01108 2.38 1.068 53.7 73.5
## 2022 2.28 0.638 8.98 2.39 0.01050 2.29 0.769 55.3 85.2
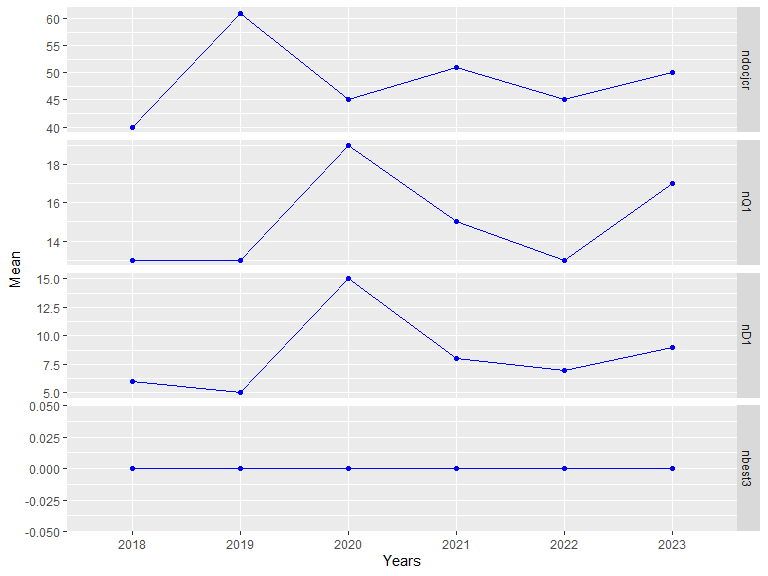
## 2023 1.98 0.520 9.38 2.21 0.01349 2.97 0.830 58.4 103.7
##
## Documents in JCR:
## 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023
## 40 61 45 51 45 50
##
## Documents in Q1:
## 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023
## 13 13 19 15 13 17
##
## Documents in D1:
## 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023
## 6 5 15 8 7 9
##
## Documents in top 3 journals:
## 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023
## 0 0 0 0 0 0Note: res1$docjcrcat contains the combined queries.
Variable list
The following list shows all variables used in the database tables:
Note: The table above was generated using the
datatable() function from the DT package. By default, the
first rows are displayed. Click on the page index (below) to change
this. You can sort by column by clicking on the arrows to the right of
its name. You can search for values (search box, top right) and filter
values (click on the filter box below the name of each variable).